
It is concluded that research on retrograde amnesia research is still in its infancy, as the neural correlates of memory storage are still unknown. These memory disorders have prompted a considerable research effort aimed at finding animal models to characterize the functional role of these critical brain. The pattern of memory disturbance and slowed information processing resembled deficits generally observed in subcortical dementias, such as Huntington's disease, but in addition, the patients with multiple sclerosis showed naming difficulties that are usually associated with cortical dementias, such as Alzheimer's disease. Questions such as why recovery from retrograde amnesia can occur in retrograde (dissociative) amnesia, and why long-term new learning of episodic-autobiographic episodes is possible, are addressed. Author Hans J Markowitsch 1 Affiliation 1 Physiological Psychology, University of Bielefeld, Bielefeld, Germany. The proportion of impaired patients was quite similar for anterograde and remote memory tests and for recall and recognition procedures. More than 45% of the patients scored below the tenth percentile. More than 75% of the patients scored below the tenth percentile for controls on the Symbol-Digit Modalities Test, while 61% scored below the tenth percentile on verbal fluency. fellow at the Boston University Memory Disorders Research Center. Deficits were most striking on the Symbol-Digit Modalities Test and the verbal fluency measures, tests that require rapid information processing. The clinical features of anterograde and retrograde amnesia are an important source of.
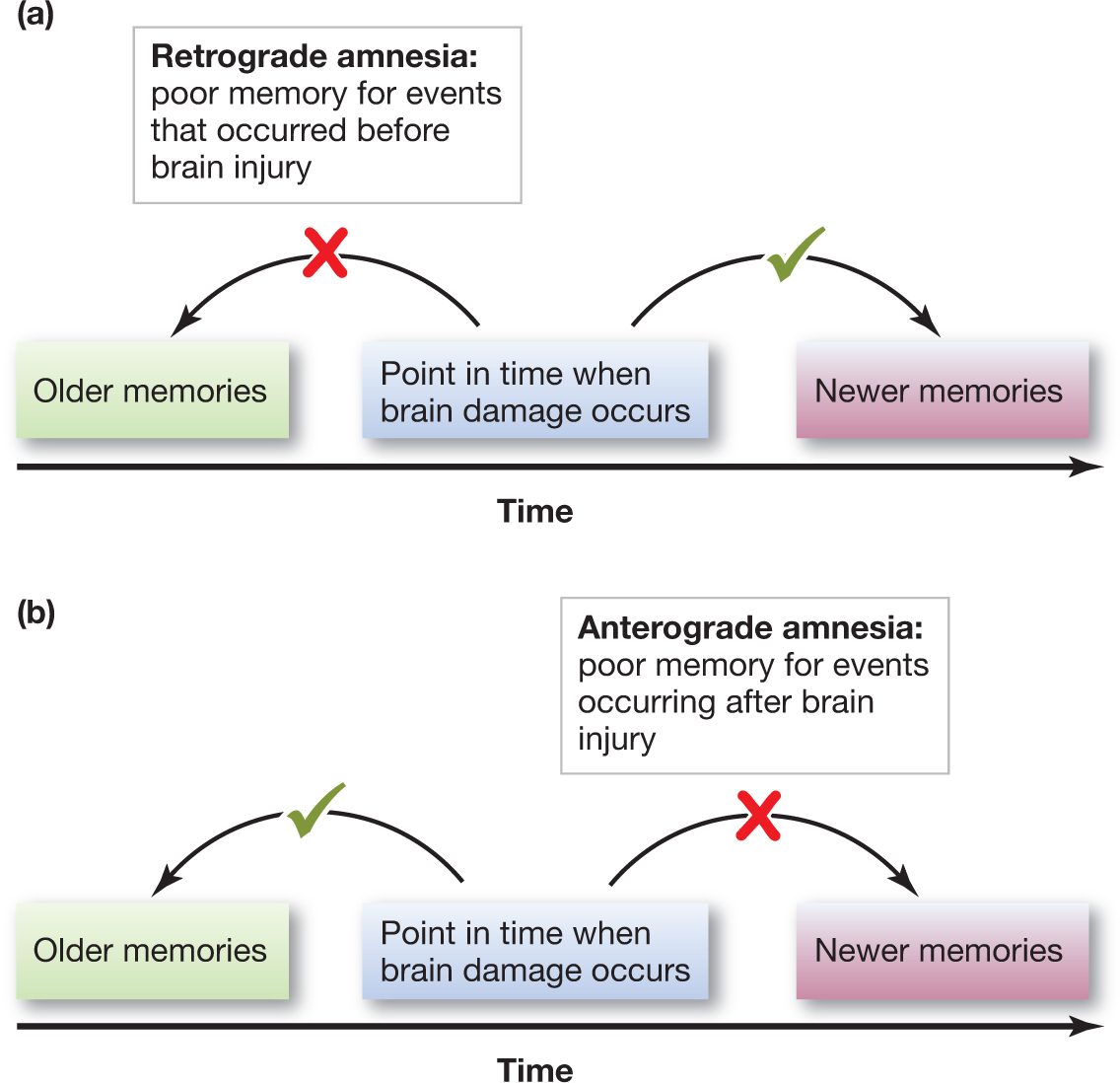
Although there were marked differences in the extent and severity of cognitive disturbance among individual patients, as a group they were impaired compared with controls on all measures. Synaptic Correlates of Anterograde Amnesia and Intact Retrograde Memory in a Mouse Model of Alzheimers. The performance of 38 patients with chronic progressive multiple sclerosis was compared with that of 26 age- and education-matched controls on a battery of tests of information-processing speed, verbal fluency, naming, egocentric perception, and anterograde and remote memory.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
